Chayu Yang
Mathematical modeling, analysis, and simulation of Cholera dynamics
A Dissertation Presented for the Doctor of Philosophy in Computational Science: Computational and Applied Mathematics, The University of Tennessee at Chattanooga
Chayu Yang, August 2020
Abstract:
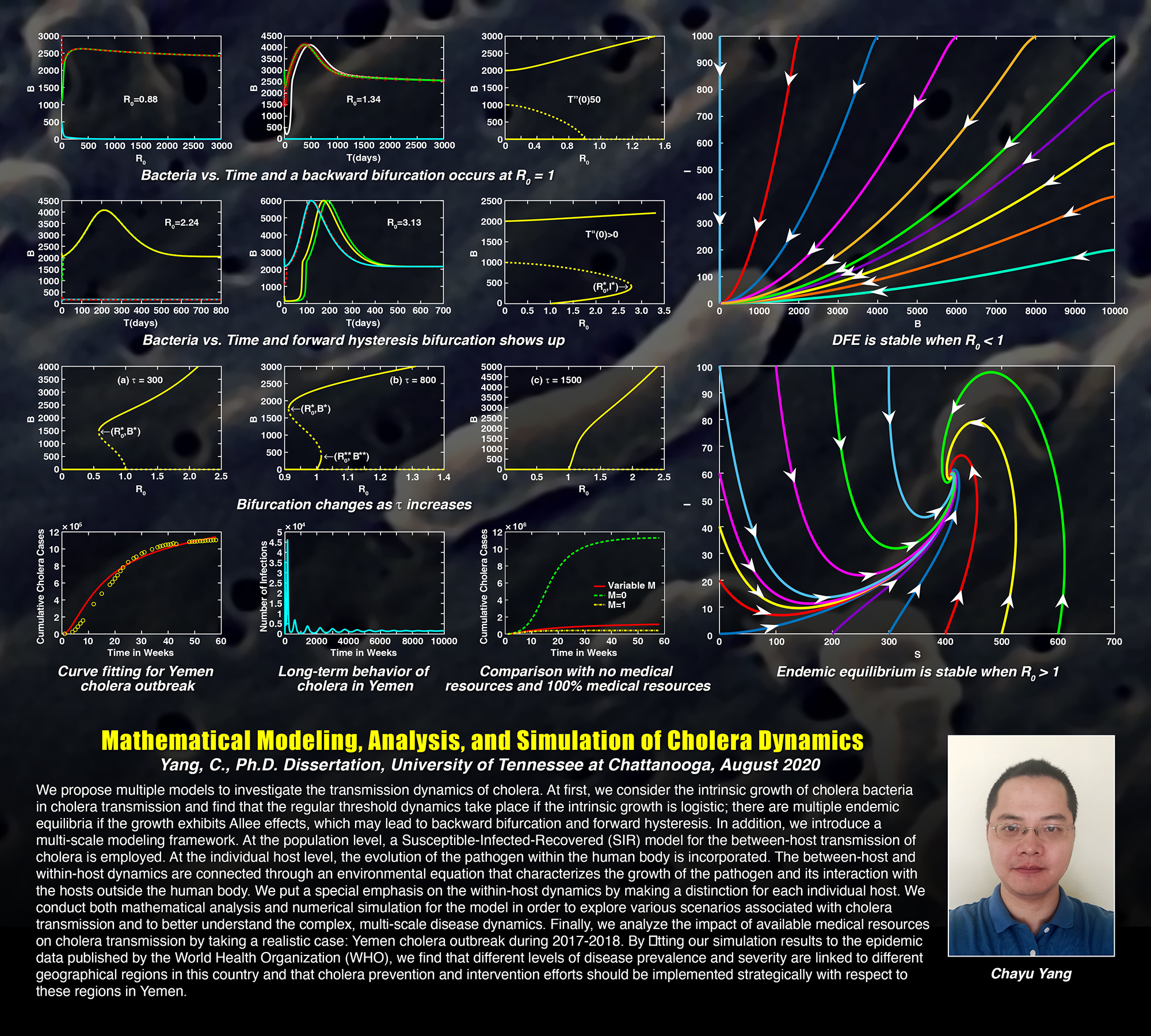
We propose multiple models to investigate the transmission dynamics of cholera. At first, we consider the intrinsic growth of cholera bacteria in cholera transmission and find that the regular threshold dynamics take place if the intrinsic growth is logistic; there are multiple endemic equilibria if the growth exhibits Allee effects, which may lead to backward bifurcation and forward hysteresis. In addition, we introduce a multi-scale modeling framework. At the population level, a Susceptible-Infected-Recovered (SIR) model for the between-host transmission of cholera is employed. At the individual host level, the evolution of the pathogen within the human body is incorporated. The between-host and within-host dynamics are connected through an environmental equation that characterizes the growth of the pathogen and its interaction with the hosts outside the human body. We put a special emphasis on the within-host dynamics by making a distinction for each individual host. We conduct both mathematical analysis and numerical simulation for the model in order to explore various scenarios associated with cholera transmission and to better understand the complex, multi-scale disease dynamics. Finally, we analyze the impact of available medical resources on cholera transmission by taking a realistic case: Yemen cholera outbreak during 2017-2018. By fitting our simulation results to the epidemic data published by the World Health Organization (WHO), we find that different levels of disease prevalence and severity are linked to different geographical regions in this country and that cholera prevention and intervention efforts should be implemented strategically with respect to these regions in Yemen.
Click here to access a copy of Chayu's dissertation.